Open Research Europe is an open access publishing pla tform for the publication of research stemming from Horizon 2020 and Horizon Europe funding across all subject areas. The platform makes it easy for Horizon 2020 and Horizon Europe beneficiaries to comply with the open access terms of their funding. It offers researchers a publishing venue to share their results and insights rapidly and facilitate open, constructive research discussion. The research, which is submitted to Open Research Europe, is published and, then, it is submitted to peer review following an invitation. In this way, the process is fast, transparent and open, while maintaining the highest research publication standards.
tform for the publication of research stemming from Horizon 2020 and Horizon Europe funding across all subject areas. The platform makes it easy for Horizon 2020 and Horizon Europe beneficiaries to comply with the open access terms of their funding. It offers researchers a publishing venue to share their results and insights rapidly and facilitate open, constructive research discussion. The research, which is submitted to Open Research Europe, is published and, then, it is submitted to peer review following an invitation. In this way, the process is fast, transparent and open, while maintaining the highest research publication standards.
It should be noted that ORE is constantly evolving and some changes might not reflect in our guides. The last update was made on August 27, 2021.
Submissions
Open Research Europe publishes articles across the Natural Sciences, Engineering and Technology, Medical Sciences, Agricultural Sciences, Social Sciences and Humanities. Articles which are submitted at this point will be published in March 2021 when the operation of the ORE platform is officially announced. You can consult the publication policies for every subject area on Open Research Europe. A relevant article and data guide can be found below.
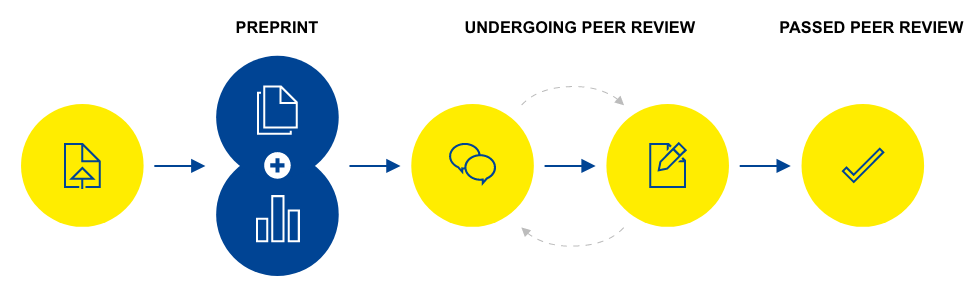
Submission: The submission of the article and its data is made through a relevant system. The editorial team carries out a comprehensive set of prepublication checks to ensure that all policies and ethical guidelines are adhered to.
Prepublication: Once the article has undergone the set of prepublication checks, the preprint version is published within 10 days, enabling immediate viewing and citation.
Peer review: Next, expert reviewers are invited to an open peer review procedure during which their names, their comments and observations together with the authors’ responses and the comments of registered users are published alongside the article. Authors are encouraged to publish revised versions of their article (see below). All the versions of the article are linked and independently citable.
Following peer review: Finally, articles that pass peer review are sent to major index databases and repositories.
On the ORE platform, each publication submitted must have at least one author who has been or still is, a recipient of a Horizon 2020 grant from the European Commission. What is more, the article to be published must be a result of that project.
As in other publication systems, the work has to be original, although articles posted on a preprint server such as arXiv, SSRN, BioRxiv, MedRxiv, etc. can be submitted for publication in Open Research Europe. It must meet all applicable research and publication standards (for details, see here). Authors must also submit the original research data that will allow other researchers to replicate the research or part of it (for details, see here).
Authors must have understood Open Research Europe’s policies for article publication and its publishing model, which requires authors to actively suggest suitable peer reviewers for their article until at least two reviews have been received. Authors must include their information in full along with their affiliation information, and a conflict of interest statement, as well.
Articles can be submitted as Word (doc or docx) or rich text format (rtf) files. For LaTeX, submit a ZIP file of the project, which must also include the PDF. If you have any questions about suitable file formats, please email us.
One-minute guide on how to submit on the platform
Publications types
There are certain submission criteria for every article across all subject areas and guidelines for the authors, as well.
The following article types concern all subject areas of agricultural and veterinary sciences, engineering and technology, medical and health sciences and natural sciences.
Research articles
Research Articles should present original findings, such as the results of basic and translational research, clinical and epidemiologic studies, or clinical trials, as well as qualitative and observational research. Null and negative findings, as well as re-analyses and replications of previous studies leading to new results, are all encouraged.
Brief Reports
Brief Reports include single-finding papers that can be reported with one or two illustrations (figures/tables), descriptions of unexpected observations, and lab protocols.
Data notes
Data Notes are brief descriptions of scientific datasets that promote the potential reuse of research data and include details of why and how the data were created; they do not include any analyses or conclusions.
Method articles
Method Articles describe new experimental, statistical, or computational methods, or tests/procedures in basic, translational or applied research, and should have been well tested. This includes new study methods, substantive modifications to existing methods or innovative applications of existing methods to new models or research questions. We welcome technical articles that describe tools that facilitate the design or performance of experiments, provide data analysis features or assist medical treatment such as drug delivery devices.
Software tool articles
A Software Tool Article should include the rationale for the development of the tool and details of the code used for its construction. The article should provide examples of suitable input data sets and include an example of the output that can be expected from the tool and how this output should be interpreted.
Study protocols
Study Protocols describe in detail any study design, including (but not limited to) experimental design of basic, translational and applied research, clinical trials or systematic reviews. All protocols for randomised clinical trials must be registered and follow the SPIRIT guidelines. Study pre-protocols (i.e. discussing provisional study designs) may also be submitted and will be clearly labelled as such when published. Study Protocols for pilot and feasibility studies may also be considered.
Registered reports
Registered Reports are a form of empirical article in which the methods and proposed analyses are published and reviewed prior to research being conducted. This format seeks to neutralise a variety of inappropriate research practices, including inadequate statistical power, and selective reporting of results. These articles are denoted by a Registered Report label.
Reviews
Reviews should provide a balanced and comprehensive overview of the latest discoveries in a particular subject area.
Systematic reviews
Systematic Reviews should usually be based on medical interventions or animal model studies. Systematic Reviews should deal with a clearly formulated question and use systematic and explicit methods to identify, select, and critically assess the relevant research. Systematic Reviews should be written following the PRISMA reporting guidelines.
Clinical practice articles
Clinical Practice Articles describe case series (i.e. group or series of case reports involving patients who were given similar treatment), but should not be based on a single case (single cases are published as Case Reports).
Case reports
A medical Case Report should be original and provide adequate detail of a single patient case. It does not need to describe an especially novel or unusual case as there is benefit from collecting details of many standard cases.
Case studies
Case Studies are a process or record of research into the development of a person, group or situation over a period of time. They are an empirical inquiry that investigates research application through real-life context or imagined scenarios A description of a legal case or a hypothetical case study used as a teaching exercise would also fit into this category.
The following article types concern all subject areas of the arts and the humanities.
Research articles
Research articles focus on theoretical and empirical research. This could include original research and creative work in the arts and humanities.
Essays
Essays are analytic or interpretive literary opinions on a single topic. This could include work outlining a reflective argument or a personal point of view.
Reviews
Reviews should provide concise and precise updates on the latest scholarship in a given area of arts and humanities research.
Research articles
Research Articles should present original findings, such as market research or surveys, qualitative and observational studies, empirical, scientific or clinical research. Null and negative findings and reanalysis of previous studies leading to new results, as well as confirmatory results, are encouraged.
Essays
Essays are analytic or interpretive compositions on a single topic. This could include articles outlining an argument or personal point of view.
Case studies
Case Studies are a process or record of research into the development of a person, group or situation over a period of time. They are an empirical inquiry that investigates research application through real-life context or imagined scenarios A description of a legal case or a hypothetical case study used as a teaching exercise would also fit into this category.
Brief reports
Brief Reports are small, often preliminary studies, that contain only essential references, and minimal tables and figures, placing full attention on empirical methods, results and data analysis, and the implications of those results. Brief Reports focus on issues of methodology and observation.
Method articles
Method Articles describe new experimental, observational, or computational methods and should have been well tested. This includes new study methods, substantive modifications to existing methods or innovative applications of existing methods to new models or research questions.
Study protocols
Study Protocols describe in detail any study design, including (but not limited to) experimental design of basic and applied research, systematic reviews, or protocols defining research questions and empirical methods. Study pre-protocols (i.e. discussing provisional study designs) may also be submitted and will be clearly labelled as such when published. Study Protocols for pilot and feasibility studies are also considered.
Registered reports
Registered Reports are a form of empirical article in which the methods and proposed analyses are published and reviewed prior to research being conducted. This format seeks to neutralise a variety of inappropriate research practices, including inadequate statistical power, and selective reporting of results. These articles are denoted by a Registered Report label.
Data notes
Data Notes are brief descriptions of scholarly datasets that promote the potential reuse of scholarly data and materials and include details of why and how the data were created; they do not include any analyses or conclusions.
Software tool articles
A Software Tool Article should include the rationale for the development of the tool and details of the code used for its construction. The article should provide examples of suitable input data sets and include an example of the output that can be expected from the tool and how this output should be interpreted.
Systematic reviews
Systematic Reviews in the social sciences should deal with a clearly formulated question and use systematic and explicit methods to identify, select, and critically assess the relevant research.
Reviews
Reviews should provide a balanced and comprehensive overview of the latest discoveries in a particular subject area.
What is a new version?
Publication in Open Research Europe is much more dynamic than in traditional journals and our articles are still “developing” after the authors’ initial version is published. To distinguish more clearly between different types of article versions, we label them with the following badges:
- Revised: It indicates a new version that usually incorporates changes in response to the reviewers’ comments.
- Update: is a new version, often after the article is indexed and/or the peer review is considered complete, in which authors can add small developments relevant to the research discussed in that article.
